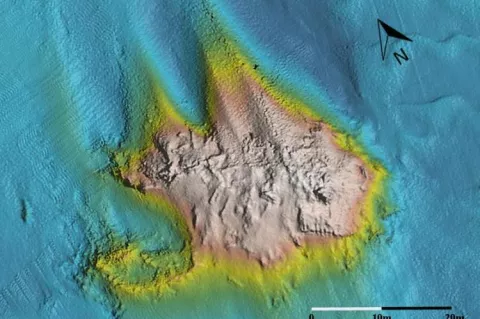
Scapa Flow Wrecks: Multibeam Sonar Survey & 3D Photogrammetry
Scapa Flow, located in the Orkney Islands of Scotland, is the site of the scuttling of the High Seas Fleet of the Imperial German Navy in June 1919 at the end of World War I. While many of the wrecks were salvaged following the war, the remaining wrecks have become popular dive sites. In recent times, efforts to learn more about these wrecks through multibeam sonar surveys and 3D photogrammetry have taken place. Rosemary E.